Unveiling the intricacies of genetic inheritance, the Punnett squares x-linked answer key serves as a beacon of clarity in understanding the transmission of X-linked traits. This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamental principles of Punnett squares, empowering individuals to unravel the genetic tapestry of life.
As we embark on this journey, we will explore the intricacies of X-linked inheritance, deciphering the genetic blueprints that shape our existence. Through step-by-step guidance and real-world applications, this discourse will illuminate the significance of Punnett squares, equipping readers with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of genetic inheritance.
Punnett Squares for X-Linked Inheritance: Punnett Squares X-linked Answer Key
A Punnett square is a diagram that predicts the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring based on the genotypes of their parents. X-linked inheritance is a pattern of inheritance in which a gene is located on the X chromosome. Because males only have one X chromosome, they are more likely to express X-linked recessive traits than females.
Punnett Square Construction, Punnett squares x-linked answer key
To construct a Punnett square for X-linked inheritance, follow these steps:
- Write the genotype of the female parent along the top of the square and the genotype of the male parent along the side.
- Fill in the squares with the possible gametes that each parent can produce. For females, this will be either X or Xa. For males, this will be either X or Y.
- Combine the gametes to form the possible genotypes of the offspring.
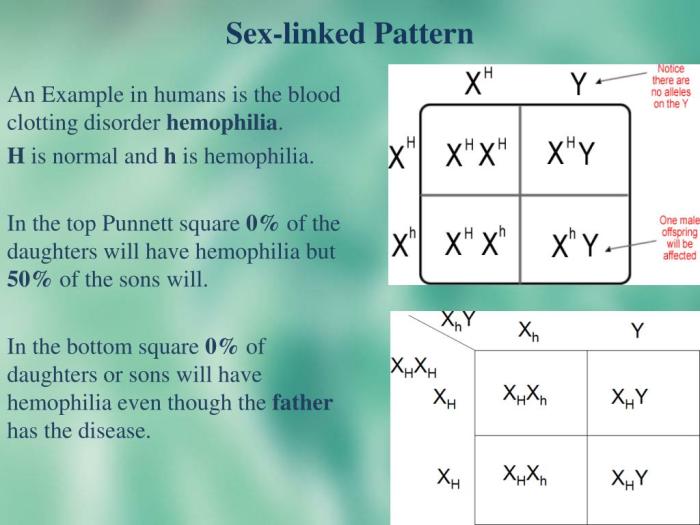
Example:A woman who is heterozygous for an X-linked recessive trait (X aX) mates with a man who is hemizygous recessive (X aY). The Punnett square for this cross is:
| Xa | Y | |
|---|---|---|
| Xa | XaXa | XaY |
| X | XXa | XY |
Genotype and Phenotype Analysis
The genotype of an offspring is the combination of alleles that it inherits from its parents. The phenotype is the observable expression of the genotype. For X-linked traits, there are three possible genotypes:
- XX:homozygous dominant, female
- XaX a: homozygous recessive, female
- XaY: hemizygous recessive, male
For X-linked recessive traits, males are more likely to express the recessive phenotype because they only have one X chromosome. Females, on the other hand, are more likely to be carriers of the recessive allele.
Real-World Applications
Punnett squares are used in a variety of real-world scenarios, including:
- Genetic counseling:Punnett squares can be used to help couples understand the risk of having a child with a genetic disorder.
- Medical diagnosis:Punnett squares can be used to help diagnose genetic disorders.
However, it is important to note that Punnett squares are only a theoretical tool. They do not take into account all of the factors that can affect inheritance, such as the environment and gene interactions.
FAQ Overview
What is the purpose of a Punnett square?
A Punnett square is a diagram that predicts the possible genotypes of offspring based on the genotypes of their parents.
What is X-linked inheritance?
X-linked inheritance is a pattern of inheritance in which genes located on the X chromosome are passed from parents to offspring.