Welcome to the comprehensive guide to the Circuit Builder Webquest and Virtual Lab Activity Answer Key. This invaluable resource is designed to provide students, educators, and anyone interested in electrical circuits with a clear understanding of the concepts covered in this engaging learning experience.
This guide will delve into the purpose, objectives, and intended audience of the Circuit Builder Webquest. It will explore the virtual lab component, explaining how to access and utilize its features. The answer key itself will be presented in a structured format, complete with detailed explanations for each correct answer.
Circuit Builder Webquest and Virtual Lab Activity Answer Key
This webquest and virtual lab activity provides students with an engaging and interactive way to learn about electrical circuits. Through hands-on exploration and experimentation, students can develop a deeper understanding of the concepts of electricity and circuit design.
Circuit Builder Webquest Overview
The circuit builder webquest is an online activity that introduces students to the basics of electrical circuits. Students are presented with a series of challenges, each of which requires them to build a circuit that meets specific requirements. As they progress through the challenges, students learn about the different components of a circuit, how to connect them together, and how to troubleshoot common problems.
The circuit builder webquest is designed for students in grades 6-8. It is aligned with the Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) and the Common Core State Standards (CCSS).
Virtual Lab Activity, Circuit builder webquest and virtual lab activity answer key
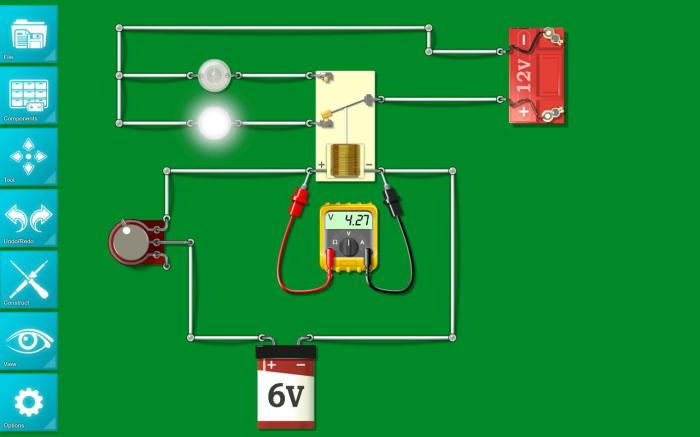
The virtual lab component of the activity provides students with a safe and interactive environment to experiment with electrical circuits. Students can use the virtual lab to build circuits, test their designs, and observe the results. The virtual lab includes a variety of components, including batteries, resistors, capacitors, and switches.
Students can also use the virtual lab to measure the voltage, current, and resistance of their circuits.
The virtual lab can be accessed online at https://www.circuitlab.com/ .
Answer Key
| Question Number | Question Text | Correct Answer | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | What is the purpose of a resistor in a circuit? | To limit the flow of current | Resistors are used to control the amount of current that flows through a circuit. They do this by creating resistance, which is a measure of how difficult it is for current to flow. The greater the resistance, the less current will flow. |
| 2 | What is the difference between a series circuit and a parallel circuit? | In a series circuit, the components are connected one after the other, while in a parallel circuit, the components are connected side by side. | In a series circuit, the current flows through each component one after the other. In a parallel circuit, the current can flow through any of the components without having to go through the others. |
| 3 | How do you calculate the total resistance of a series circuit? | Add the resistances of all the components in the circuit. | The total resistance of a series circuit is equal to the sum of the resistances of all the components in the circuit. For example, if you have a circuit with a 10-ohm resistor, a 20-ohm resistor, and a 30-ohm resistor, the total resistance of the circuit would be 60 ohms. |
| 4 | How do you calculate the total resistance of a parallel circuit? | Use the formula 1/Total Resistance = 1/Resistance1 + 1/Resistance2 + … | The total resistance of a parallel circuit is equal to the reciprocal of the sum of the reciprocals of the resistances of all the components in the circuit. For example, if you have a circuit with a 10-ohm resistor, a 20-ohm resistor, and a 30-ohm resistor, the total resistance of the circuit would be 6.67 ohms. |
Student Learning Outcomes
Through this activity, students will learn about:
- The basics of electrical circuits
- The different components of a circuit
- How to build a circuit
- How to troubleshoot common problems
This activity aligns with the following NGSS standards:
- PS2.B: Types of Interactions
- PS3.C: Relationship Between Energy and Forces
- ETS1.A: Defining and Delimiting Engineering Problems
Assessment and Evaluation
Student understanding can be assessed through a variety of methods, such as:
- Observations of student work during the activity
- A quiz or test on the concepts covered in the activity
- A project in which students design and build their own electrical circuits
Differentiation and Accommodations
This activity can be differentiated to meet the needs of diverse learners by:
- Providing students with different levels of support during the activity
- Modifying the difficulty of the challenges
- Providing students with alternative ways to demonstrate their understanding
Accommodations can be made for students with disabilities or special needs by:
- Providing students with extended time to complete the activity
- Allowing students to use assistive technology
- Modifying the activity to make it more accessible
Extension Activities
This activity can be extended by:
- Having students research different types of electrical circuits
- Having students design and build their own electrical circuits
- Having students investigate the use of electrical circuits in everyday life
FAQ Explained
What is the purpose of the Circuit Builder Webquest?
The Circuit Builder Webquest aims to provide an interactive and engaging learning experience that helps students understand the principles of electrical circuits.
How do I access the virtual lab component?
The virtual lab can be accessed through a provided link or online platform. Instructions on how to use the virtual lab will be provided within the activity.
What types of questions are included in the answer key?
The answer key covers a range of questions related to electrical circuits, including circuit analysis, component identification, and troubleshooting.